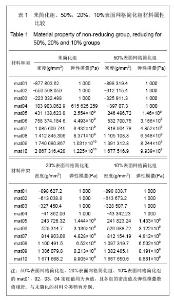
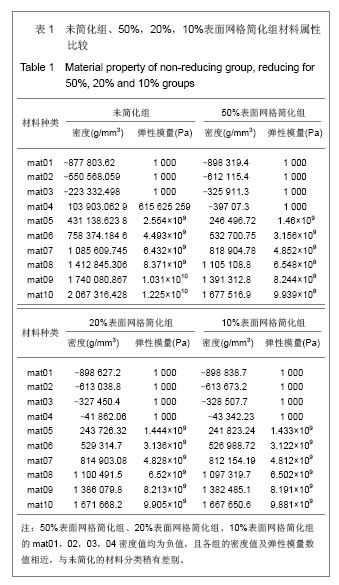
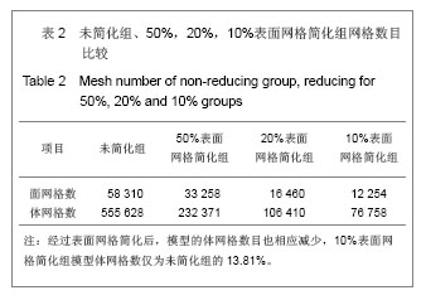
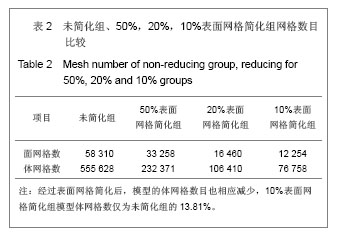
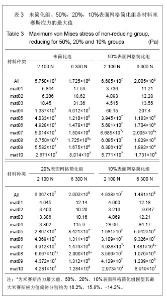
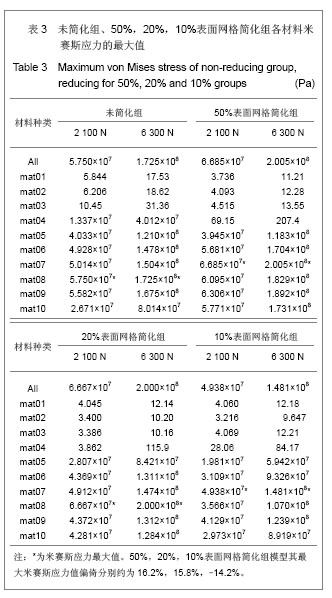
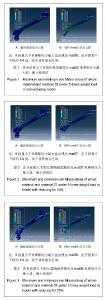
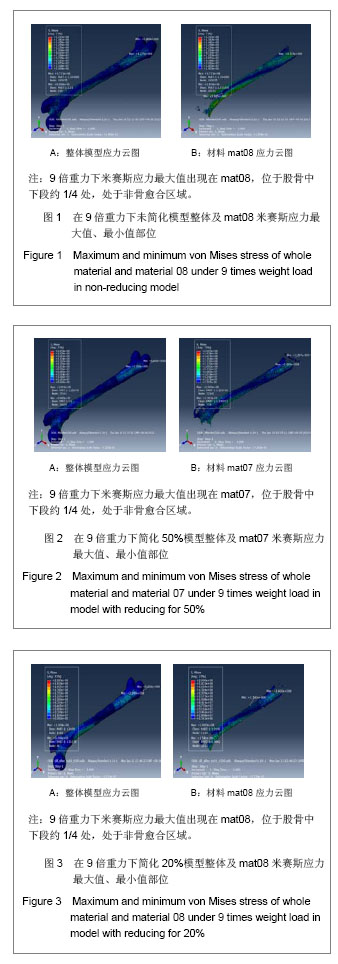
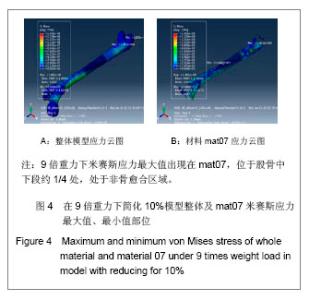
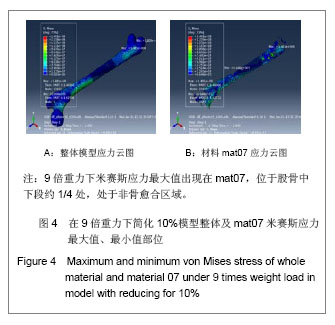
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (39): 6926-6931.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.39.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fast establishment of bone healing finite element model of femoral fracture treated by intramedullary nail fixation for 1 year
Zhou Jiang-jun1 , Zhu Zhi-yu1, Zhao Min1, Yan Ya-bo2, Lei Wei2, Lü Ren-fa1, Yu Wei-tao1, Zhang Li1, Chen Rong-jian1
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, the 184th Hospital of PLA, Yingtan 335000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2 Department of Orthopedics, Xijing Hospital, the Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Online:2013-09-24Published:2013-09-24 -
Contact:Zhao Min, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the 184th Hospital of PLA, Yingtan 335000, Jiangxi Province, China zhaomin184@sina.com -
About author:Zhou Jiang-jun★, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, the 184th Hospital of PLA, Yingtan 335000, Jiangxi Province, China zhoujiangjun@hotmail.com -
Supported by:Nanjing Military Medical Technology Innovation Project, No. 10MA058*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Jiang-jun, Zhu Zhi-yu, Zhao Min, Yan Ya-bo, Lei Wei, Lü Ren-fa, Yu Wei-tao, Zhang Li,Chen Rong-jian. Fast establishment of bone healing finite element model of femoral fracture treated by intramedullary nail fixation for 1 year[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(39): 6926-6931.
share this article
| [1]徐云钦,冯水云,梁再跃,等.三种内固定在股骨干骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2002,4(4):316-317.
[2]魏卫,廉红星,张连青.锁定加压接骨板微创治疗下肢长骨干粉碎性骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(7):631-633.
[3]宫岩虎,卢延胜,付廷友,等.交锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折(附45例报告)[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(2):109-112.
[4]刘志华,管文浩,檀中奇.基于CT图像构建的腰椎三维有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(26):4760-4764.
[5]Taylor WR, Roland E, Ploeg H, et al. Determination of orthotropic bone elastic constants using FEA and modal analysis. J Biomech. 2002;35(6):767-773.
[6]Cimerman M, Kristan A. Preoperative planning in pelvic and acetabular surgery: The value of advanced computerised planning modules. Injury. 2007;38:442-449.
[7]扈延龄,金丹,苏秀云,等.基于三维CT数据的髋臼骨折计算机辅助虚拟手术设计[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(2):137.
[8]杜长岭,马信龙,马剑雄,等. 利用有限元分析股骨颈骨折内固定术后前倾角变化对股骨近端力学的影响[J].医用生物力学,2012, 27(6):603-607.
[9]Wang JY, Zhang QH, Lupton C,等.个体化骨盆模型的建立、有限元分析及试验验证(上)[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(2):222- 224.
[10]Wang JY,Zhang QH,Lupton C,等.个体化骨盆模型的建立、有限元分析及试验验证(下)[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(3):318-320.
[11]Ling X,Said R,Young P,et al.基于图像处理的个性化建模:从医学扫描到高精度计算模型的转换[J].医用生物力学,2008, 23(1): 31-36.
[12]樊黎霞,丁光兴,费王华,等.基于CT图像的长管骨有限元材料属性研究及实验验证[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(1):102-108.
[13]杜长岭,马信龙,马剑雄,等. 利用有限元分析股骨颈骨折内固定术后前倾角变化对股骨近端力学的影响[J].医用生物力学,2012, 27(6):603-607.
[14]Lengsfeld M, Schmitt J, Alter P, et al. Comparision of geometry-based and CT voxel-based finite element modelling and experimental validation. Med Eng Phys. 1998;20(7): 515-522.
[15]张国栋,廖维靖,陶胜祥,等.股骨有限元分析附材料属性的方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(43):8436-8441.
[16]张国栋,林海滨,陈宣煌,等. 股骨颈骨折预测的Ansys非线性屈曲分析[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(4):738-740.
[17]王大忠,余正红,周民强,等. 3D膝关节模型的构建[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(48):8945-8949.
[18]王彭,吕洪海,杜智军,等. 儿童股骨三维立体模型的构建[J]. 中国数字医学, 2012,7(7):111-113.
[19]Burkhart TA, Andrews DM, Dunning CE. Finite element modeling mesh quality, energy balance and validation methods: A review with recommendations associated with the modeling of bone tissue. J Biomech. 2013;46(9):1477-1488.
[20]陈纪宝,奚春阳,焦力刚,等. 有限元分析在腰椎生物力学应用中的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(26):4908-4912.
[21]Lin D,Li D, Li W, et al. Dental implant induced bone remodeling and associated algorithms. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2009;2(5):410-432.
[22]李小康,郭征,刘继鹏. 低弹性模量接骨板固定股骨干骨折的有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(12):1164-1168.
[23]张先龙,王小平,喻鑫罡,等.主动负重和被动加载时骨折局部动力学环境的比较研究[J],中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(3): 258-262.
[24]申华,陈国振,王建国.振动应力下兔尺骨及骨痂的三维有限元应力与振动分析[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2001,20(2): 182-186.
[25]Steiner M, Claes L, Simon U, et al. A computational method for determining tissue material properites in ovine fracture calluses using electronic speckle pattern interferometry and finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2012;34(10): 1521-1525.
[26]Vetter A, Liu Y, Witt F, et al. The mechanical heterogeneity of the hard callus influences local tissue strains during bone healing: afinite element study based on sheep experiments. J Biomech. 2011;44(3):517-523.
[27]史俊. 实验性兔下颌骨骨折愈合过程的研究——生物力学仿真模型的建立[D]. 上海交通大学医学院,2006.
[28]Weis JA, Granero- Moltó F, Myers TJ, et al. Comparison of microCT and an inverse finite element approach for biomechanical analysis: results in amesenchymal stem cell therapeutic system for fracture healing. J Biomech. 2012; 45(12):2164-2170.
[29]Zeng ZL, Cheng LM, Zhu R, et al. Building an effective nonlinear three-dimensional finite-element model of human thoracolumbar spine. Chin J Orth. 2011;91(31): 2176-2180.
[30]Sitthiseripraip K, Van Oosterwyck H, Vander Solten J, et al. Finite element study of trochanteric gamma nail for trochanteric fracture. Med Eng Phys. 2003;25(2):99-106. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||